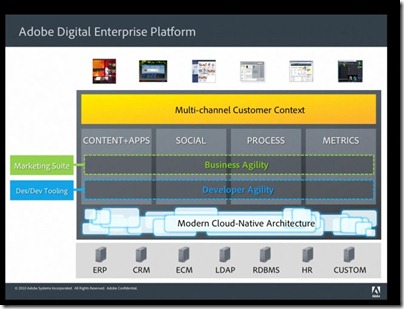
Adobe has announced its Digital Enterprise Platform for Customer Experience Management. My tip to Adobe: that is too many words with too many syllables for busy IT people who are trying to get their work done. What on earth is it? The same old stuff repackaged, or something genuinely new?
The answer is a bit of each. Adobe has made several big acquisitions over the last few years, starting with the Macromedia merger in 2005 that really formed a new Adobe, bringing together digital publishing and the Flash platform. In September 2009 Adobe acquires Omniture for web analytics, and in October 2010 Day Software. This last one seems to be having a huge impact. Day’s product is called CQ5 Web Content Management and is built on CRX, a content repository which conforms to JCR 2.0 (Java Technology API 2.0), a Java API. Here’s Roy Fielding, formerly at Day and now Principal Scientist at Adobe, from this white paper [pdf]:
The Content Repository API for Java Technology (JCR) is poised to revolutionize the development of J2SE/J2EETM applications in the same way that the Web has revolutionized the development of network-based applications. JCR’s interface designers have followed the guiding principles of the Web to simplify the interactions between an application and its content repository, thus replacing many application-specific or storage-specific interfaces with a single, generic API for content repository manipulation.
JCR is a boon for application developers. Its multipurpose nature and agnostic content model encourages reuse of the same code for many different applications, reducing both the effort spent on development per application and the number of interfaces that must be learned along the way. Its clean separation between content manipulation and storage management allows the repository implementation to be chosen based on the actual performance characteristics of the application rather than some potential characteristics that were imagined early in the application design. JCR enables developers to build full-featured applications based on open source implementations of a repository while maintaining compatibility with the proprietary repositories that are the mainstay of large data centers.
Adobe already has an application platform based on LiveCycle Enterprise Suite, which you will notice now redirects to the Digital Enterprise Platform. Ben Watson, Adobe’s Principal Customer Experience Strategist, explained it to me like this:
The core of the platform now becomes the repository that we got from the Day acquisition. We are also following their leadership around the use of RESTful technology, so changing how we do our web services implementation, how we do our real time data integration into Flash using data services. There’s really four technologies at play here. There’s CQ5, Adobe LiveCycle which is all the business process management on the back end, the online marketing suite with Omniture, and Creative tools which allow to both design and develop all of this content and assets … We had two Java platforms and we brought them into one.
You can read up on the Digital Enterprise Platform here or see a chart of capabilities here. Much of it does look like rebranding of existing LiveCycle modules; but as a statement of direction it is an interesting one.
Is this for on-premise deployment, or cloud hosted? Adobe has a tie-up with Amazon for hosted deployment, though there is no no multi-tenant hosting from Adobe yet; I got the impression from Watson that it is being worked on.
Adobe is aware that it does not stand alone, and there are several connectors and integration points for third-party applications, such as a SAP data services connector.
Adobe also has a series of “solutions”, which are permutations of web content management, analytics, document processing, social media and so on. There is also a Unified Workspace, currently in beta, which is a dashboard application.
The company’s line is that it is well placed to address the challenge of the mobile revolution, and to bring greater usability and social interaction to business applications, the consumerization of IT.
Although that sounds a strong pitch, melding all this together into something new while keeping hold of existing developers and designers is a challenge. Another issue for Adobe is that the company’s strong presence in design, multimedia and marketing makes it hard to appeal to more general enterprise developers. Nevertheless, the combination of Fielding’s influence and Adobe’s strength in design, documents and cross-platform clients makes this a platform worth watching.