I’ve been trying Office 2010. I use Outlook with Exchange 2007 and was interested to see how it compares to Outlook 2007.
In terms of things I care about, not much has changed. That said, it took me a long time to wrest good performance out of Outlook 2007 – which is why this blog is a top Google hit on “slow outlook 2007” – whereas the speed of Outlook 2010 seems fine right out of the box. I haven’t tried all the permutations though: cached and non-cached, 32 or 64 bit, and so on, so consider this only a preliminary impression.
One of the reasons is that the Outlook team has abandoned integration with Windows Desktop Search for online mailboxes:
The Search Toolbar add-in setup code is removed in Outlook 2010. The Search Toolbar add-in enables local indexing of online mode Exchange Server mailbox stores by using Windows Desktop Search. As a result of this change, e-mail in online Exchange mailboxes will not appear in the results of Windows Explorer searches. The online indexing add-in is a legacy component that adversely affects performance of Outlook during startup and shutdown. With this removed in Outlook 2010, users will experience improved Outlook reliability and significantly lower Exchange bandwidth usage. For fast search, use Cached Exchange Mode or for online mode, use Exchange Search in Exchange 2007 and later versions.
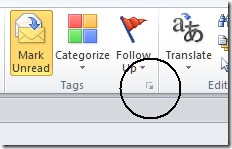
So what else is new? You can see a technical summary here. Outlook has now had the full Ribbon treatment, which I suppose is good for consistency, though plenty of annoyances remain. For example, let’s say you’re trying to figure out whether an email is genuine or not. I had one that gave me pause for thought, supposedly from Amazon.com. The first thing I check is the message header – no, not the thing Outlook still calls the “message header”, which adds a couple of fields to the top bar. What I need to see is the email header, showing the origin of the message and its path across the Internet. I clicked around hopefully. Eventually I found it – you have to click the down arrow at bottom right of the Tags (huh?) section of the ribbon:
This opens what Outlook calls Properties, including the “Internet headers” which are what I want to see. The message was spam, by the way – it came from a domain that has nothing to do with Amazon:
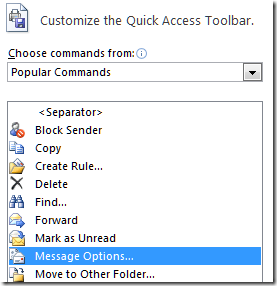
Fortunately you can add this dialog to the Quick Access Toolbar. Simply go to Customize Quick Access Toolbar –> More commands, and add the Properties command. Except it’s not called Properties. The dialog is called Properties, but the command is called Message Options…
I am so used to this sort of thing with Outlook that I expect it; Outlook 2010 is no worse than its predecessor.
[Update: Ed Bott points out in the comments that you can also get to the Properties dialog through the File tab.]
Other new features include Quick Step macros – could be handy though I can’t think of a reason I will use it; connection to multiple Exchange accounts which will be excellent for those who need it, especially if you can use cached mode with all of them (I’ve not checked); and a bunch of stuff that only lights up if you have Exchange Server 2010, such as (at last) server-based archiving – no more archive.pst files littered around every machine you ever use.
I do want to mention one persistent disappointment though. Conversation view. Why can’t Outlook behave like a discussion forum, where each thread is grouped? In theory it can: just switch on Conversation View. In practice it is useless, because instead of using the In-Reply-To field that identifies a message which is a reply to another message, Outlook 2010 uses the subject line.
The subject line is hopeless as a means of defining conversations. Worse, it’s dangerous. Let’s say you’ve got an unimportant “conversation” with the subject “June 20th” – it’s about a meeting you don’t need to attend. Then you get an email also entitled “June 20th” from someone else; this one is critically important. By grouping it into the existing “conversation”, Outlook disguises its importance.
I recall being told at Microsoft’s PDC last November that the Outlook team was aware of this problem in the preview and it would be fixed somehow. However, when I switched Conversation View on briefly in Outlook 2010 RTM I saw exactly the same problem. I suppose there is a chance that upgrading to Exchange 2010 magically fixes it; this on the to-do list for me. For now, the solution is not to use Conversation View at all.