Smartphone power has made another jump forward with the announcement at CES in Las Vegas of new devices built on NVIDIA’s new Tegra 2 package – a System on a Chip (SoC) that includes dual-core CPU, GPU, and additional support for HD video encoding and decoding, audio, imaging, USB, PCIe and more:
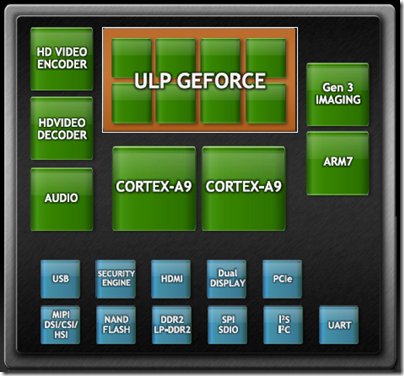
The CPU is the ARM Cortex-A9 which has a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) architecture and a 32-bit instruction set. It also supports the Thumb-2 instruction set which is actually 16-bit. How is 16-bit an upgrade over 32-bit? Well, 16-bit instructions means smaller code, even though it gets translated to 32-bit instructions at runtime:
For performance optimised code Thumb-2 technology uses 31 percent less memory to reduce system cost, while providing up to 38 percent higher performance than existing high density code, which can be used to prolong battery-life or to enrich the product feature set.
The GPU is an “ultra low power” (ULP) 8-core GeForce. In essence, the package aims for high performance with low power consumption, exactly what is wanted for mobile computing.
Power is also saved by sophisticated power management features. The package uses a combination of suspending parts of the system, gating the clock speed, screen management, and dynamically adjusting voltage and frequency, in order to save power. The result is a system which NVIDIA claims is 25-50 times more efficient than a typical PC.
According to NVIDIA, Tegra 2 enables web browsing up to two times faster than competitors such as the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8250 or Texas Instruments OMAP 3630 – though of course these companies also have new SoCs in preparation.
Tegra 2 is optimised for some specific software. One is the OpenGL graphics API. “The job of the GPU is to implement the logical pipeline defined by OpenGL”, I was told at an NVIDIA briefing.
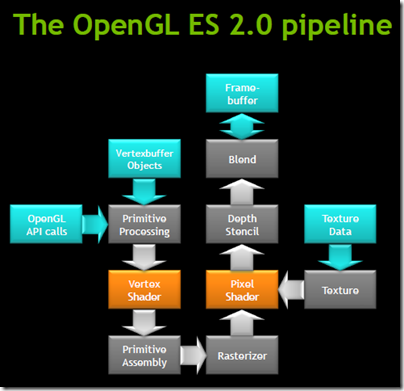
I asked whether this meant that Tegra 2 is sub-optimal for Microsoft’s Direct X API; but NVIDIA says it is sufficiently similar that it makes no difference.
Nevertheless, Tegra 2 has been designed with Android in mind, not Windows. There are a couple of reasons for this. The main one is that Android has all the momentum in the market; but apart from that, Microsoft partnered with Qualcomm for Windows Phone 7, which runs on Snapdragon, shutting out NVIDIA at the initial launch. NVIDIA is a long-term Microsoft partner and the shift from Windows Mobile to Android has apparently cost NVIDIA a lot of time. The shift took place around 18 months ago, when NVIDIA saw how the market was moving. That shift “cost us a year to a year and a half of products to market”, I was told – a delay which must include changes at every level from hardware optimisation, to designing the kind of package that suits the devices Android vendors want to build, to building up knowledge of Android in order to market effectively to hardware vendors.
Despite this focus, Microsoft demonstrated Windows 8 running on Tegra during Steve Ballmer’s keynote, so this should not be taken to mean that Windows or Windows CE will not run. I still found it interesting to hear this example of how deeply the industry has moved away from Microsoft’s mobile platform.
Microsoft should worry. NVIDIA foresees that “all of your computing needs are ultimately going to be surfaced through your mobile device”. Tegra 2 is a step along the way, since HDMI support is built-in, enabling high resolution displays. If you want to do desktop computing, you sit down at your desk, pop your mobile into a dock, and get on with your work or play using a large screen and a keyboard. It seems plausible to me.
During the press conference at CES we were shown an example of simultaneous rich graphic gaming on PC, PlayStation 3, and Tegra 2 Smartphone.

Alongside Android, Tegra 2 is optimised for Adobe Flash. NVIDIA has been given full access to the source of the Flash player in order to deliver hardware acceleration.
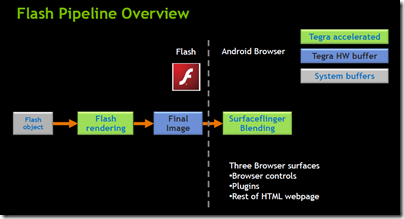
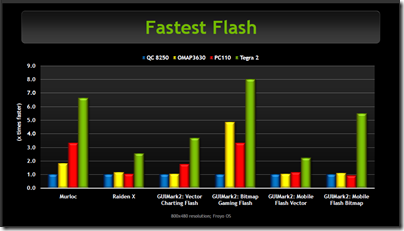
Actual devices
What about actual devices? Two that were shown at CES are the LG Optimus 2X:

and the Motorola Atrix 4G:

Both sport impressive specifications; though the Guardian’s Charles Arthur, who attended a briefing on the Atrix 4G, expresses some scepticism about whether HD video (which needs a large display) and the full desktop version of FireFox are really necessary on a phone. Apparently the claimed battery life is only 8 hours; some of us might be willing to sacrifice a degree of that capability for a longer battery life.
Still, while some manufacturers will get the balance between cost, features, size and battery life wrong, history tells that we will find good ways to use these all this new processing and graphics power, especially if we can get to the point where such a device, combined with cloud computing and a desktop dock, becomes the only client most of us need.
NVIDIA says that over 50 Android/Tegra 2 products are set to be released by mid-2011, in tablet as well as Smartphone form factors. I’m guessing that at least some of these will be winners.







