At CES in Las Vegas today NVIDIA’s CEO Jen-Hsun Huang announced the company’s first CPU: Project Denver. This is a partnership with ARM, to create “a full custom processor” targeting “high performance computing – servers, PCs, super-computers, cloud computing.” NVIDIA will still licence ARM processors for mobile computing.
Since ARM has in the past focused on the mobile and embedded market, and NVIDIA on GPUs, it is a departure for both companies.
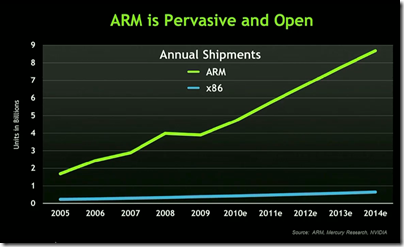
Why? Huang says it is because ARM is “the new standard microprocessor architecture.” Judging by this chart, shown at the press briefing, it is hard to disagree:
In a few years, said Huang, “There will be more ARM processors shipped than all the x86 chips ever shipped.”
NVIDIA’s press release explains that the purpose of Project Denver is to extend the range of ARM systems upwards:
For several years, makers of high-end computing platforms have had no choice about instruction-set architecture. The only option was the x86 instruction set with variable-length instructions, a small register set, and other features that interfered with modern compiler optimizations, required a larger area for instruction decoding, and substantially reduced energy efficiency.
Denver provides a choice. System builders can now choose a high-performance processor based on a RISC instruction set with modern features such as fixed-width instructions, predication, and a large general register file. These features enable advanced compiler techniques and simplify implementation, ultimately leading to higher performance and a more energy-efficient processor.
The other interesting aspect of Project Denver is its integration with the GPU – as you would expect from NVIDIA:
An ARM processor coupled with an NVIDIA GPU represents the computing platform of the future. A high-performance CPU with a standard instruction set will run the serial parts of applications and provide compatibility while a highly-parallel, highly-efficient GPU will run the parallel portions of programs.
While we tend to focus most on power efficiency for mobile devices, because we notice how long our batteries last, it is equally important for larger systems. Power consumption and dealing with heat is a key issue for datacentres, while in everyday desktop computing power consumption is a significant proportion of the running cost of an IT system.
Project Denver puts a different spin on Microsoft’s Windows-on-ARM announcement today. The assumption is that Microsoft has in mind a mobile future for Windows; but if Denver takes off it could be important on desktops and servers as well.
Before getting too excited, it is worth recalling how Intel’s Itanium, cruelly dubbed the Itanic, mostly failed in the market. That was partly thanks to design problems, and partly because the industry was too deeply hooked into x86 applications. I also recall Motorola’s doomed attempts to sell Windows NT on PowerPC in the mid Nineties.
Denver could fare better, thanks to the ubiquity of ARM in the mobile world. That said, much will depend on whether a Denver-based system really does offer significant benefits over whatever Intel and/or AMD will have come up with by the time it ships. If it is less than spectacular, Denver will be a hard sell.